Kathmandu Valley Location Analysis
Comprehensive Site Assessment for AquaSai MSR Deployment on Bagmati River
Comprehensive Site Assessment for AquaSai MSR Deployment on Bagmati River
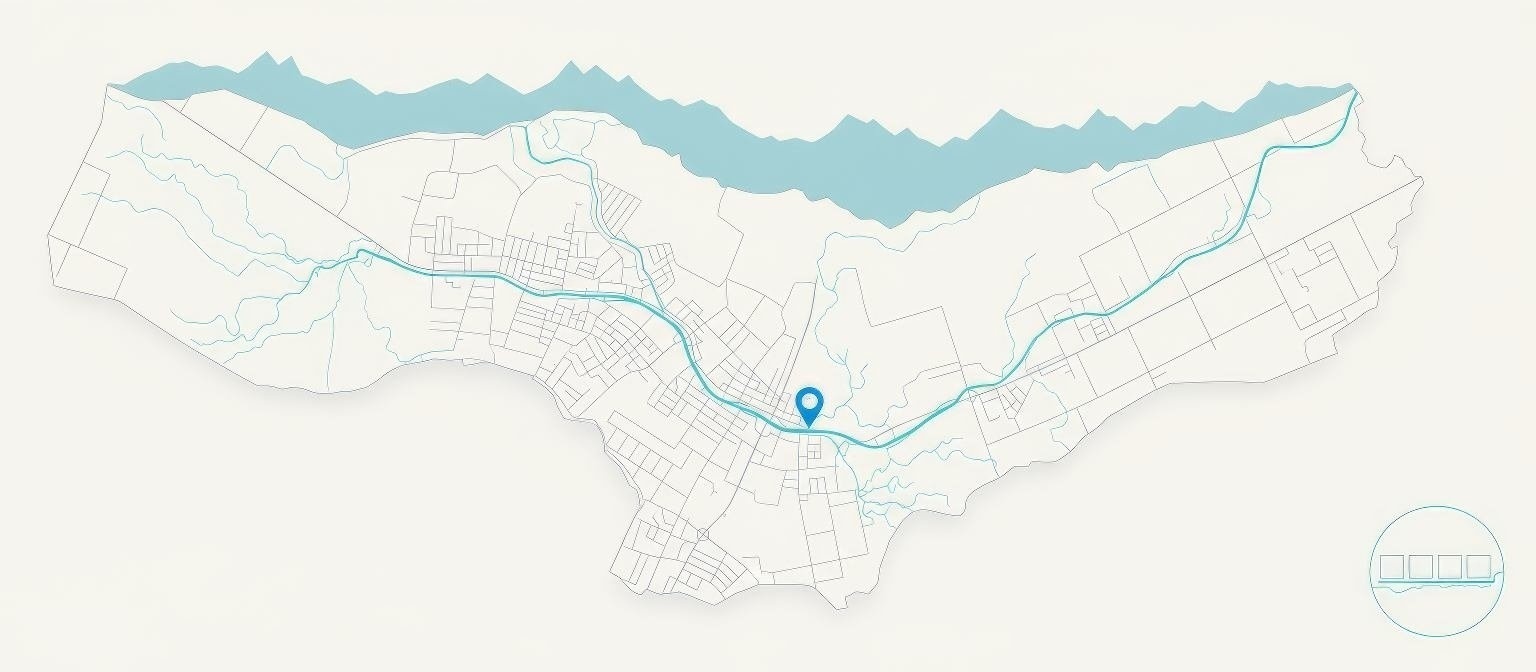
The Kathmandu Valley is an oval-shaped basin in central Nepal, home to over 3 million people. The Bagmati River, Nepal's sacred lifeline, flows through the heart of this valley, making it an ideal location for AquaSai's pioneering MSR technology deployment.
Severe Pollution Crisis: BOD levels exceed 120 mg/L (vs. 6 mg/L standard), near-zero dissolved oxygen, and heavy contamination with fecal coliform, heavy metals, and excess nutrients.
High-Impact Demonstration: Kathmandu Valley offers the perfect setting to showcase AquaSai MSR technology in a highly visible, culturally significant, and urgently needed restoration project.
Nature-Based Treatment: Multi-Stage Recirculating (MSR) constructed wetland system designed to treat 100,000 L/day in pilot phase with 99% pollutant removal efficiency.
The valley is surrounded by hills ranging from 1,500m to 2,800m elevation, creating a natural bowl that concentrates both population and pollution. The Bagmati River originates from the Shivapuri hills and flows south through Kathmandu and Lalitpur before exiting the valley at Chobar Gorge.
| Geographic Parameter | Value/Description | Implication for MSR |
|---|---|---|
| Latitude/Longitude | 27.7°N, 85.3°E | Subtropical highland climate - ideal for year-round wetland operation |
| Elevation | 1,300 - 1,500m ASL | Moderate elevation provides good temperature range for plant growth |
| Valley Area | 665 km² | Large area for multiple MSR installations and scaling |
| Average Temperature | 10-30°C (year-round) | Optimal range for wetland biological processes |
| Annual Rainfall | 1,400mm (monsoon-dominated) | Adequate water supply; monsoon management critical |
| Monsoon Season | June - September (80% of rainfall) | Design for high flow management and overflow systems |
| Dry Season | October - May | Optimal construction period; low flow treatment priority |
| Soil Type | Alluvial clay, silt, sand deposits | Suitable for constructed wetland with proper liner systems |
| Seismic Zone | High (Zone V) | Earthquake-resistant design essential for infrastructure |
| Water Table Depth | 2-10m (seasonal variation) | Groundwater protection & monitoring critical |
5.5 kWh/m²/day average solar radiation
Excellent for solar-powered pumps and UV disinfection systems. Nepal's high altitude provides strong UV intensity for natural pathogen reduction.
Valley winds: Upslope during day, downslope at night
Natural aeration benefit for wetland systems. Minimal odor transport concern with proper design.
Bagmati flow: 5-50 m³/s (seasonal variation)
High variability requires flexible intake design and storage capacity for consistent treatment.
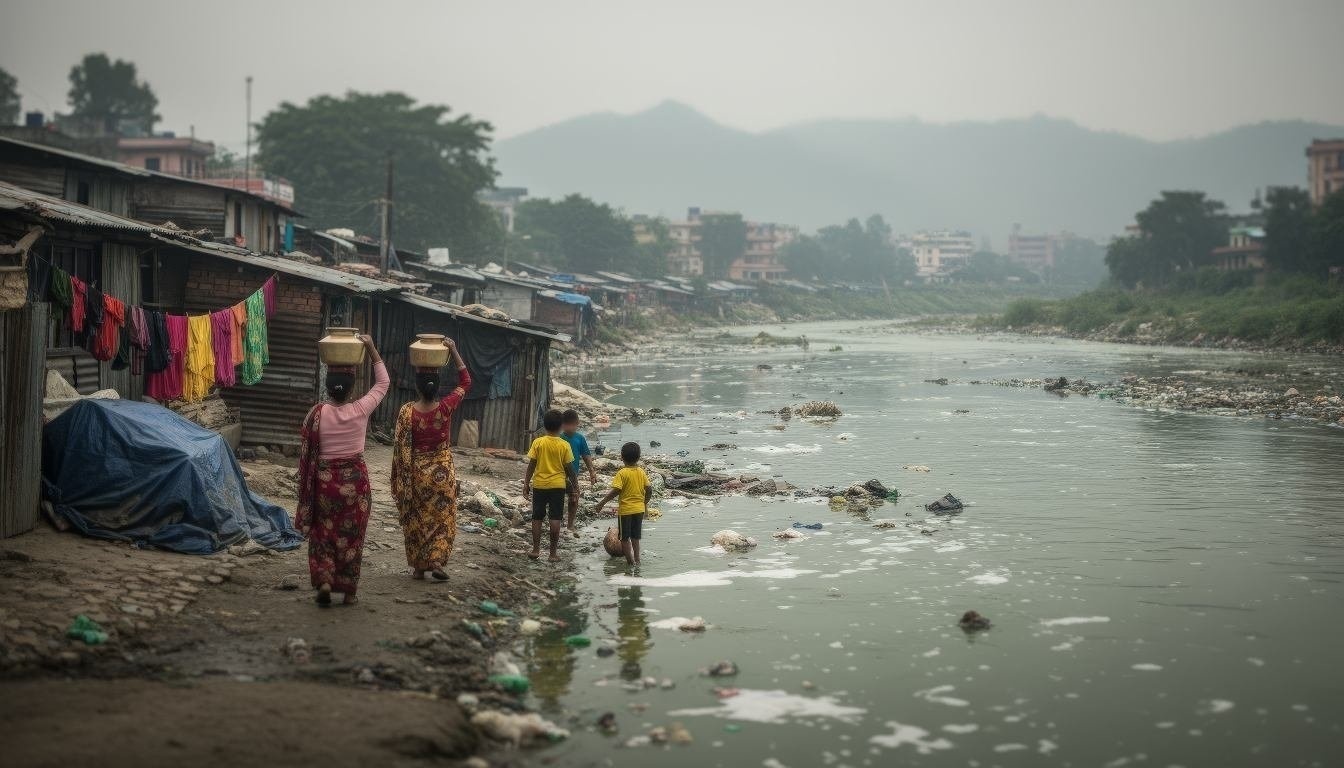



The Bagmati River in Kathmandu Valley is classified as Class V (worst quality) with extreme pollution requiring urgent intervention.
| Parameter | Current Level | Standard | MSR Target | Removal % |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BOD (mg/L) | 120+ | 6 | 10-15 | 88-92% |
| COD (mg/L) | 200+ | 30 | 40-50 | 75-80% |
| DO (mg/L) | 0-1 | 5-6 | 4-6 | 5-6x increase |
| TSS (mg/L) | 150-300 | 50 | 30-40 | 80-87% |
| TN (mg/L) | 40-80 | 10 | 8-12 | 80-85% |
| TP (mg/L) | 5-15 | 0.5 | 1-2 | 80-90% |
| Fecal Coliform (MPN/100mL) | 10⁶-10⁷ | 1,000 | 10³-10⁴ | 99%+ |
| Heavy Metals (Pb, Cd, Cr) | Above limits | Varies | Within limits | 60-90% |
AquaSai has identified 48 native Nepali plant species suitable for MSR deployment in Kathmandu Valley climate, including:
| Total Footprint: | 2,000 m² |
| Treatment Capacity: | 100,000 L/day |
| Wetland Cells: | 4 stages |
| Depth: | 0.6-1.2m |
| Retention Time: | 5-7 days |
| Recirculation Rate: | 3-5x |
Each stage optimized for specific pollutant removal mechanisms
| Component | Specification | Quantity | Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Civil Works | Excavation, terracing, concrete structures | 2,000 m² | $85,000 |
| Liner System | HDPE 1.5mm, geotextile underlay | 2,500 m² | $15,000 |
| Filter Media | Graded gravel (20-80mm), sand (2-5mm) | 200 m³ | $8,000 |
| Pumps & Piping | Solar pumps, PVC pipes, valves | Complete system | $25,000 |
| Anaerobic Digester | Fixed dome, 20m³ capacity | 1 unit | $15,000 |
| Plant Materials | Native phytoremediation species | 10,000 plants | $10,000 |
| Monitoring Equipment | DO, pH, turbidity, flow meters | 1 set | $12,000 |
| Labor & Training | Skilled & unskilled labor, workshops | 12 months | $30,000 |
| TOTAL CAPEX | $200,000 | ||
Minimal energy footprint: MSR system requires only 2 kW for recirculation pumps, easily provided by solar panels. Annual energy cost: $200 (vs. $5,000+ for conventional treatment).
Energy production: Biogas from anaerobic digester produces 50 m³/day, equivalent to 1,000 kWh/month - net positive energy balance.
AquaSai has conducted comprehensive site analysis across Kathmandu Valley, evaluating locations based on:
Guhyeshwari Temple Area is recommended for initial pilot deployment due to:
Phase 1: Single pilot site (Year 1)
Phase 2: 3 additional sites (Years 2-3)
Phase 3: 10+ sites valley-wide (Years 4-5)
Target: Treat 20% of Bagmati River flow by Year 5

Present concept to HPCIDBC, Ministry of Water Supply, and KUKL. Secure letter of support and land identification assistance.
Engage municipal bodies for land allocation. Conduct community consultations. Submit environmental clearance applications.
Formalize MOUs with government partners. Engage ADB/World Bank for co-financing. Sign academic collaboration agreements.
Regular stakeholder briefings. Community training programs. Media engagement. Progress reporting to all partners.
| Treated Water Sales | $20,000/yr |
| To farmers (irrigation) | $0.05/m³ |
| To industries (cooling) | $0.10/m³ |
| Biogas Sales | $15,000/yr |
| To local households | $1/m³ |
| Medicinal Plant Harvest | $8,000/yr |
| Ayurvedic herbs | Various |
| Carbon Credits | $5,000/yr |
| VCS/Gold Standard | $10/ton CO₂e |
| Training & Consulting | $2,000/yr |
| TOTAL ANNUAL REVENUE: $50,000 | |
| Personnel | $18,000/yr |
| 1 Manager, 2 Technicians | |
| Plant Maintenance | $5,000/yr |
| Replanting, pruning, harvest | |
| Equipment & Repairs | $6,000/yr |
| Pumps, sensors, tools | |
| Energy | $200/yr |
| Solar panels maintenance | |
| Monitoring & Testing | $4,000/yr |
| Water quality lab tests | |
| Administration | $1,800/yr |
| TOTAL ANNUAL OPEX: $35,000 | |
AquaSai MSR deployment operates as a hybrid social enterprise with multiple value propositions:
Financial sustainability achieved through diversified revenue streams and low operating costs, with $15K annual surplus for system expansion and community development programs.
| Cost Comparison | AquaSai MSR | Conventional WWTP | Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| CAPEX (per 100,000 L/day) | $200,000 | $650,000 | 69% |
| Annual OPEX | $35,000 | $120,000 | 71% |
| Energy Cost | $200/yr | $5,000/yr | 96% |
| Chemical Cost | $0 | $15,000/yr | 100% |
| Skilled Labor Required | Low | High | 60% less |
| Land Footprint | 2,000 m² | 800 m² | Creates green space |
| Co-Benefits | Multiple | None | Ecosystem value |
| Water Quality | 80-90% pollutant removal |
| Treatment Volume | 100,000 L/day sustained |
| System Uptime | 95%+ operational days |
| Community Benefit | 50+ households served |
| Jobs Created | 10 direct, 30 indirect |
| Land Irrigated | 5 hectares productive |
| Biogas Production | 50 m³/day average |
| Stakeholder Satisfaction | 80%+ positive feedback |
Water Quality Testing (Weekly):
Operational Monitoring (Daily):
Impact Monitoring (Quarterly):
AquaSai is committed to open-source knowledge sharing to maximize impact across Nepal and globally: